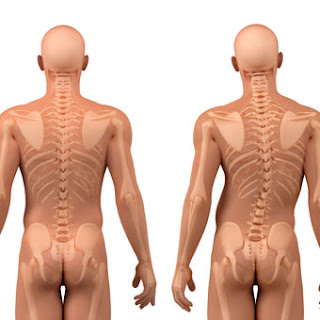
Scoliosis is a disorder in which the body frame in the form of spinal curvature. As many as 75-85% of scoliosis cases are idiopathic, the disorder of unknown cause. While the other 15-25% of scoliosis cases are the side effects caused due to suffering from specific disorders, such as muscular dystrophy, Marfan syndrome, Down syndrome, and other diseases. The disorder causes various muscles or nerves around the spinal cord does not function perfectly and causing the spine becomes curved shape.
Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention for Scoliosis
1. Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to the suppression of pain.
Purpose: The pattern of breathing Effectively.
Plan of action:
2. Acute Pain: back related to the position of lateral body tilt.
Purpose: Pain is reduced or lost
Plan of action:
Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention for Scoliosis
1. Ineffective Breathing Pattern related to the suppression of pain.
Purpose: The pattern of breathing Effectively.
Plan of action:
- Assess respiratory status every 4 hours.
- Help and teach the patient to breath in any one hour. Rationale: Increasing the maximum ventilation and oxygenation.
- Adjust bed semi-Fowler position to improv lung expansion. Rational: Sitting height allowing Easier breathing and lung expansion.
- Monitor vital signs every 1 hour. Rational: general indicators, circulation status and adequacy of perfusion.
2. Acute Pain: back related to the position of lateral body tilt.
Purpose: Pain is reduced or lost
Plan of action:
- Assess the type, intensity and location of pain. Rational: Influencing choice / control the effectiveness of Interventions can influence the level of anxiety to pain.
- Teach relaxation and distraction techniques. Rational: To divert attention, thereby reducing pain.
- Teach and Encourage use of the brace. Rational: To Reduced pain during activity
- Collaboration in the provision of analgesia. Rational: To relieve pain.